Principal investigator: Prof. Jang-Ping Sheu
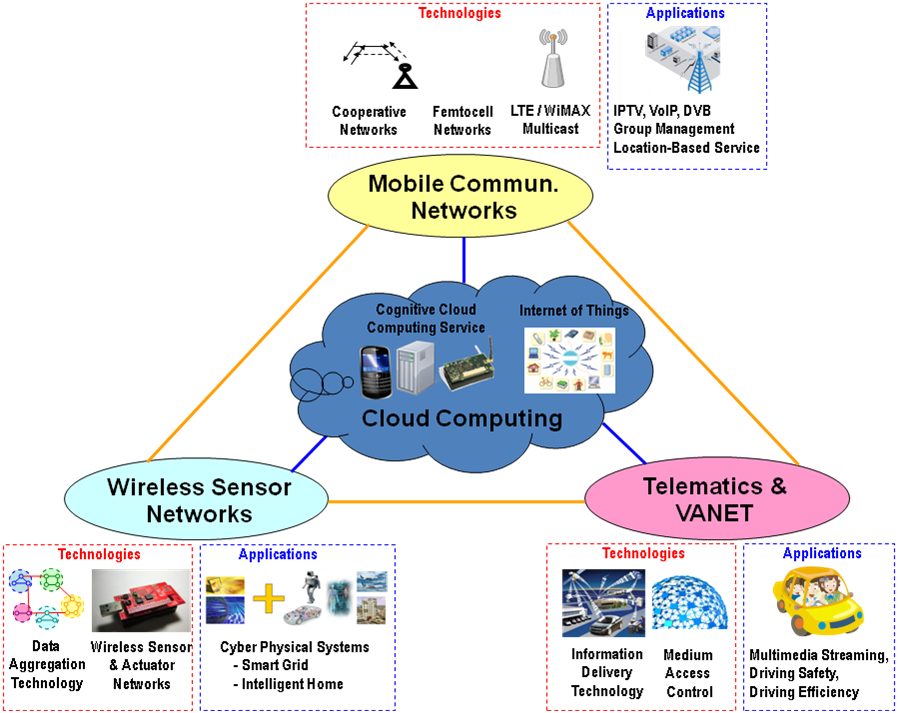
With the dramatic advances of information and communication technologies, networking services are expected to integrate heterogeneous wire-line/wireless access technologies and the Internet backbone for providing various types of applications to both mobile and stationary users. Subproject 1 aims to investigate wireless sensor networks, vehicular networks, mobile communication networks, and the applications of networking technologies to cloud computing, including “Internet of Things” and “Cyber Physical System”. As illustrated in Figure 1, Subproject 1 consists of the following research topics: Wireless Sensor Networks, Vehicular Networks, Mobile Communication Networks, and Cloud Computing which are elaborated on below.
- Wireless Sensor Networks
Due to the rapid development of micro-mechanical/electrical and sensing technology, a variety of sensing functions, such as temperature, humidity, pressure, supersonic wave, infrared, wind power, acceleration, moving direction, carbon dioxide, etc., can be embedded into wireless sensor nodes. Recently, wireless sensor networks are used in a wide range of applications, including battlefield surveillance, health care, environmental monitoring, building and bridge monitoring, and so on. The deployment, re-deployment, network self-cavity and abruption diagnosis, self-reconfiguration, data collection with charge balance, query, data integration, and other popular topics with numerous changes of parameters, such as mobility, dynamic adjustment of sensing range and communication range, target coverage, barrier coverage, area coverage, wireless transmission mode (on land light wave or submarine acoustic wave), the arrangement of sleep/wake-up mechanism, the extensions of sensing ability like the visual camera sensor networks, the direction sensing capabilities, and so on, lead the research topics on the wireless sensor network to become rich and diverse in the future. The future research topics include:
-
(1) Information brokerage systems: In the information brokerage systems, the producer stores the information it possesses, such as its coordinates and the obtained temperature and humidity information, in many brokers such that the consumer can obtain the producer's information from the nearest broker of the producer rapidly. Because the sensor node usually has no physical coordinates, establishing an effective information brokerage system in the wireless sensor network is a big challenge, and has received considerable attentions recently.
-
(2) Effective data aggregation: In wireless sensor networks, the obtained information (like temperature, humidity, and so on) usually has temporal or spatial correlation. Using temporal or spatial correlation to select the data transmission path to aggregate the obtained data such that the transmission power of the obtained data is reduced has become one of the important research topics in wireless sensor networks.
-
(3) Underwater wireless sensor networks: Underwater wireless sensor has low delivery rate, long propagation delay, low mobility rate and other features. Therefore, it is a big challenge to design an efficient routing protocol or an effective information brokerage system in an underwater wireless sensor network. Recently, the underwater wireless sensor network has become a hot research topic due to the burgeoning underwater wireless sensor applications.
-
(4) Wireless sensor and actor networks: The wireless sensor and actor networks are composed of wireless sensors and actors with a powerful functionality, such as unmanned helicopter carrying fire extinguishers and automatic vehicle carrying charging devices. The actors decide the motion and complete the task by collecting the obtained information from wireless sensors. Due to the wide application in the daily life, the wireless sensor and actor network has become one of the most popular topics in wireless sensor networks.
- Vehicular Networks
The advance of wireless communication and networking technologies, popularization of mobile devices, and dense distribution of transportation vehicles lead to the growing interest and importance in Telematics. Recognizing the potential of Telematics, there have been concerted efforts to network vehicles and a spectrum of 75MHz has been allocated, exclusively to Telematics, in USA, Japan, Europe, and many other countries. The current trends of Telematics, from the technological perspective, emphasize on vehicular ad-hoc networks (VANETs), including the vehicle to vehicle (V2V), vehicle to roadside-unit (V2R), and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) interconnections. From the application perspective, the current trends of Telematics aim to enhance vehicular safety, driving efficiency, and in-car entertainment. What follows outlines a few promising research directions:
-
(1) Information delivery technology: Broadcasting, multicasting, and routing are fundamental operations in vehicular ad-hoc networks (VANETs). Broadcasting is typically used to disseminate safety messages in a specific region; multicasting is important for fleet navigation services; and routing is a basic functionality to send packets, in a multi-hop manner, between two vehicles or between a vehicle and a road-side unit (RSU). Considering the lack of reliable and efficient information delivery technology in VANETs, important research issues include broadcast optimization, cluster planning, multicast tree construction, cooperative communication, and routing algorithm tailored to networks with highly dynamic topology and non-uniform node distribution.
-
(2) Media access control (MAC) technology: Diverse Telematics applications require various quality of service (QoS). For example, safety alerts require quick and reliable information dissemination, while multimedia applications require a high bandwidth. Important QoS metrics include throughput, delay, jitter, and a combination thereof. To assure QoS and enhance overall performance of VANETs, many challenges remain to be addressed at the forefront of designing the MAC protocol. Such research issues include opportunistic relaying, network coding, topology control, multi-channel allocation, and scheduling algorithm with QoS guarantee.
-
(3) Multimedia streaming, vehicular safety, and driving efficiency applications: Vehicular ad-hoc networks (VANETs) enable V2V, V2R, and V2I communications. Such networks present various functionalities with economic benefits in terms of vehicular safety, driving efficiency, and in-car entertainment. Such functionalities aim facilitating multimedia systems that integrate location-based services and audio/video advertisements, reducing traffic jams and accidents, enhancing efficiency of gas mileage, lowering CO2 emission, etc. However, many challenges remain to be addressed. Important challenges and research issues include: peer-to-peer multimedia streaming, file searching/sharing and application-layer multicasting; detection and dissemination of safety information; route planning/navigation and fleet management; and scheduling algorithms for heterogeneous VANETs.
- Mobile Communication Networks
In line with IMT-Advanced technology requirements and definitions in ITU-R, mobile communication networks have gradually evolved towards the fourth generation (4G). 4G/IMT-Advanced systems are expected to enable new services and usage models with higher efficiency under a highly self-configurable network infrastructure. During the evolution to 4G, WiMAX, based on IEEE 802.16 standards and the Third Generation Partnership Project’s (3GPP’s) Long Term Evolution (LTE) have been recognized as two most promising 4G candidates. While WiMAX and LTE have somewhat different designs in details, they share many common concepts, features and capabilities to meet a common set of requirements and expectations. For instance, both technologies deploy OFDMA-based designs at the physical layer combined with various modes of MIMO configurations and fast link adaptation with time-frequency scheduling. Moreover, medium access control (MAC) of both systems support multicarrier operation and heterogeneous implementation of cells, consisting of a mix of macro cells, Femtocells, and relay nodes. This brings different kinds of challenges to mobility, interference, and traffic management. Possible research directions of mobile communication networks include:
-
(1) Design of cooperative networks with high performance and quality-of-service: Cooperative communications exploit spatial diversity inherent in multiuser systems by forwarding the source’s messages to the destination cooperatively. With cooperation between users or relay stations, we are able to avoid unfavorable transmission paths and to reduce signal loss, which in turn increases transmission rate, channel capacity, and signal coverage. Cooperative relaying techniques have been adopted by the IEEE 802.16j working group to enhance coverage in WiMAX systems. In the past, most works on cooperative communications focus on the physical layer aspects of the problem. In this project, we will address the issues and challenges of cooperative networks in the MAC and higher layers. More precisely, the entire task is divided into 4 subtopics: QoS support in cooperative networks, bandwidth management in cooperative networks, the cross-layer design of cooperative networks based on MIMO techniques, and channel-aware transmission control for cooperative networks.
-
(2) Design of Femtocell networks with quality-of-service: According to the prediction from Visiongain, about 70% of the future 3G bandwidth usage will take place indoor. This phenomenon significantly affects the development trends of both network architecture and user devices. Femtocell networking, a new technology that can improve the quality of indoor mobile communication in an economic and highly efficient way, has become a popular standard to network operators. Under the concept of indoor/home networking, the future mobile devices include not only handheld equipments but also household appliances, such as printers and terminals. This boosts the amount of mobile data accesses, increasing the importance of mobile computing, data sharing, remote control and portable working environment applications in the future mobile communication. To address the new issues of home networking, 3GPP standard body is now actively developing Local IP Access (LIPA)-related specifications. Under the Femtocell networking architecture, this project will propose a telecom-based Universal LIPA solution. Possible research issues include Femtocell interference management, Femtocell access control, Femtocell/Macro cell handoff management, selected IP traffic offload, self-organizing networks, time synchronization, MIMO, emergency call, global LIPA authentication/registration, and the continuity of LIPA services.
-
(3) WiMAX/LTE multicast technology with quality-of-service: With the extensive deployment of 3G networks and the standardization of 4G technologies (including WiMAX and LTE), the demand of real-time multimedia multicast applications are increased day by day. How to support such highly bandwidth-demanding applications in an efficient way has become a very challenging problem. Layer-encoded video technique can be incorporated into multicasting to fulfill the QoS requirement in an opportunistic manner. Specifically, multimedia servers are allowed to divide video streams into layers for transmission to different base stations (BSs). The BSs can then deliver different numbers of layers to different multicast users within different multicast groups based on their current channel quality. This can opportunistically satisfy various video-quality requirements of different multicast users. This project will investigate the core technologies of WiMAX/LTE multicast mechanisms, including layer-encoded multimedia server design, opportunistic multicast scheduling and resource allocation, multi-BS synchronization and handoff, and sleep-mode power saving.
(4) Heterogeneous Networks Integration: Although different access technologies (e.g., Irda, RFID, Bluetooth, Zigbee, IEEE 802.11, 3G, WiMAX and LTE) have been proposed for different application domains, it has been envisioned that next-generation 4G mobile communication networks will be the integration of various existing and new wire-line/wireless access networks under an All-IP architecture. The integration of heterogeneous networks will further allow to realize such applications as “Internet of Things” in cloud computing. In this research topic, this project will investigate the following four aspects of heterogeneous networks integration: QoS, mobility management, security and services.
- Cloud Computing
How to develop the interoperable technology, such as internetwork gateway, so that the interoperability between hardware and driver can be established, and then applied to cloud computing for the applications of Internet of Things, sensor cloud services, and cyber physical system is an another important research issue. The research directions are described as follows:
-
(1) Internet of Things application: Because the size of sensor reduces due to the progress of micro-mechanical/electrical technology, sensors and RFID have been widely embedded in many objects in our daily lives, and have enabled a variety of objects to be able to collect and monitor the status at any time. Through the mature and wide Internet platform, the location of various objects, procedures, and conditions in the live and physical distribution applications can be accurately grasped, and be made follow-up tracking and processing, which looks like the monitor and query system of Internet of Things. Such applications face object embedded technology, IP shortage, massive data integration, fast inquiry, the establishment of flow control and feedback mechanisms, and other challenges which are the important issues needed to be overcome urgently in the future.
-
(2) Sensor cloud services: Cloud services, including have been gradually received attentions by the company in recent years. Either of “cloud” and “end” establishment mechanisms is a hot discussion topic currently. How to use a large amount of sensing information through the effective management and integration of the cloud platform, such that the technologies of sensing, transmitting, storing, and integrating can be hidden in the “cloud”, and the users in the “end” can effectively control a variety of sensing information through the convenience of inquiry and cost mechanism will be the new trend in the future.
-
(3) Cyber Physical System application: Combination of sensing technology, wireless communication technology, embedded component integration technology, real-time computing and control technology will integrate the physical world and the digital world seamlessly. Sensing and digitalizing the state of the physical world using the sensors, and reflecting in real time onto the backend control system by sensing, information integration, analysis, operations and decision-making, become one of the most popular application areas in wireless sensor networks. For example, the developments of smart living and smart electronic networks in green energy are the trends in recent years.