
計畫簡介

參與成員

研究成果

會議記錄

相關連結

回總計畫

English
Version

|
|
|
|

|
Energy Efficiency:
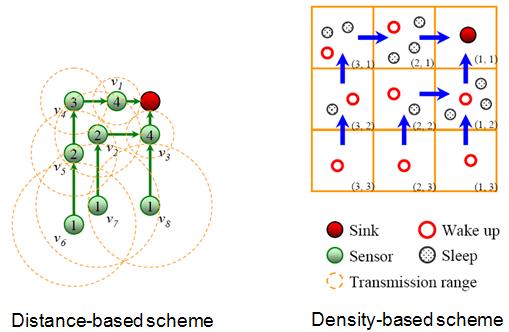
- Energy-Aware Node Placement and Topology Control Schemes for Wireless Sensor Networks
- In the WSNs, the nodes closer to the sink node have heavier traffic load for packet forwarding.
We proposed distance-based and density-based mechanisms to cope with the node placement and topology
control problem in the WSNs. The proposed schemes prolong the sensor network lifetime, balance
the power consumption of sensor nodes, and avoid collision. In addition, extension of the
proposed schemes are made from a Grid-based WSN to a randomly deployed WSN, enabling the
developed energy-balanced schemes to be generally applied to randomly deployed WSNs.
- 主要成就與成果之績效評述
- 學術或技術成就之評述
- As far as we know, this is the first study that considers both
the distance and density properties to prolong the network lifetime for a randomly
deployed WSN. This work was accepted by Computer Networks.
- An Adaptive Quorum-Based Energy Conserving Protocol for IEEE 802.11 Ad Hoc Networks
- In the IEEE 802.11 Power Saving Mode, a host must wake up at every beacon interval,
to check if it should remain awake. Such a scheme fails to adjust a host’s sleep duration
according to its traffic, thereby reducing its power efficiency. We presents new MAC
protocols for power saving in a single hop MANET. The essence of these protocols is a
quorum-based sleep/wake-up mechanism, which conserves energy by allowing the host to
sleep for more than one beacon interval, if few transmissions are involved. The
proposed protocols are simple and energy-efficiency.
- 主要成就與成果之績效評述
- 學術或技術成就之評述
- We proposed a quorum-based energy conserving Protocol for
MANETs. The results was published in the IEEE Trans. on Mobile Computing.
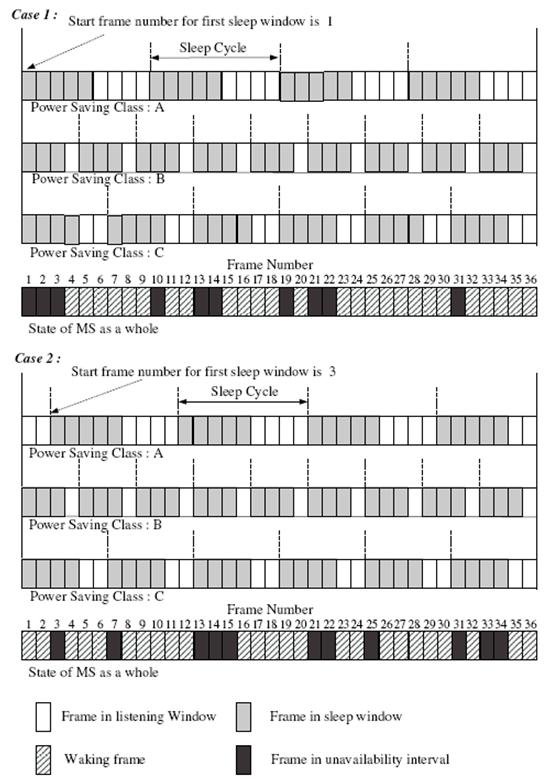
- Energy Saving Mechanism for IEEE802.16e Wireless MANs
- We have proposed an energy saving mechanism to improve the energy efficiency for the
Power Saving Class of Type II in 802.16e. It guarantees to find the maximum Unavailability
interval, during which the transceiver can be powered down. It ingeniously applies the Chinese
Remainder Theorem. Besides, a table-based algorithm is used to reduce the computational complexity
- 主要成就與成果之績效評述
- 學術或技術成就之評述
- The proposed mechanism is the first scheduling algorithm that is based
on Type II. Our solution uses a table-based method to quickly schedule to the sleeping
duration among all mobile nodes. The proposed mechanism has been accepted by IEEE
Transactions on Wireless Communications.
|
 |
|